We know that electromagnetism is an important branch of Physics that deals with electromagnetic force. It typically deals with magnetic force and electric current. Let us know about the law that relates magnetic fields to the electric current – Biot-Savart Law.
Biot-Savart’s law is an equation that gives the magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment. This segment is taken as a vector quantity known as the current element.

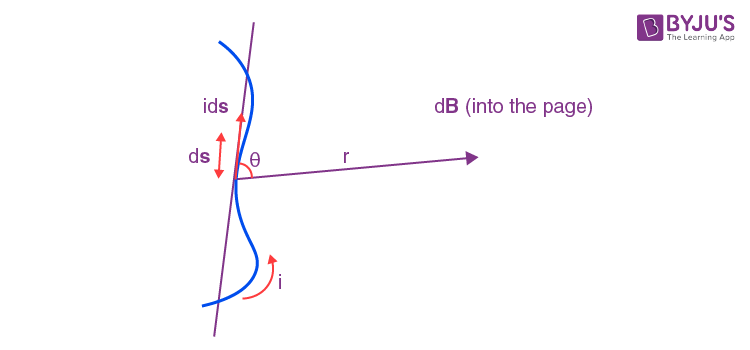
Consider a current carrying wire ‘i’ in a specific direction as shown in the above figure. Take a small element of the wire of length ds. The direction of this element is along that of the current so that it forms a vector ids.
To know the magnetic field produced at a point due to this small element, one can apply Biot-Savart’s Law. Let the position vector of the point in question drawn from the current element be r and the angle between the two be θ. Then,
\(\beginWhere, μ0 is the permeability of free space and is equal to 4π × 10 -7 TmA -1 .
The direction of the magnetic field is always in a plane perpendicular to the line of element and position vector. It is given by the right-hand thumb rule where the thumb points to the direction of conventional current and the other fingers show the magnetic field’s direction.
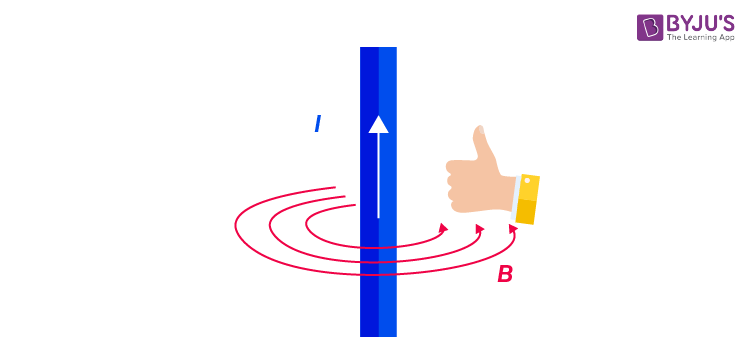
In the figure shown above, the direction of the magnetic field is pointing into the page.
Some of Biot-Savart’s Law applications are given below.
Following are the importance of the Biot-Savart law:

Q1. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic field of a wire loop at the centre of the circle with radius R and current I.
Ans: The magnitude of the magnetic field of the wire loop is given as:
\(\beginQ2. A circular coil of radius 5 × 10 -2 m and with 40 turns is carrying a current of 0.25 A. Determine the magnetic field of the circular coil at the centre.
Ans: The radius of the circular coil = 5 × 10 -2 m
Number of turns of the circular coil = 40
Current carried by the circular coil = 0.25 A
Magnetic field is given as:
\(\beginQ3. Determine the magnetic field at the centre of the semicircular piece of wire with a radius 0.20 m. The current carried by the semicircular piece of wire is 150 A.
Ans: The radius of the semicircular piece of wire = 0.20 m
Current carried by the semicircular piece of wire = 150 A
Magnetic field is given as:
\(\beginThe differential form of Biot-Savart law is given as: